Mesh Status Display
The Mesh Status page lists mesh nodes and link quality information, along with any LAN hosts and advertised services available on the network. Below the node name bar there are several controls.
The Refresh button refreshes the Mesh Status display with current information.
The Auto button sets the display to automatically refresh the node information every 10 seconds. To end auto-refresh mode, click Stop or Quit. Stop returns to the static Mesh Status display. Quit takes you back to the Node Status display, but clicking Mesh Status again from there will return you to auto-refresh mode on the Mesh Status display.
The Quit button returns you to the Node Status display.
Mesh Status Display Sections
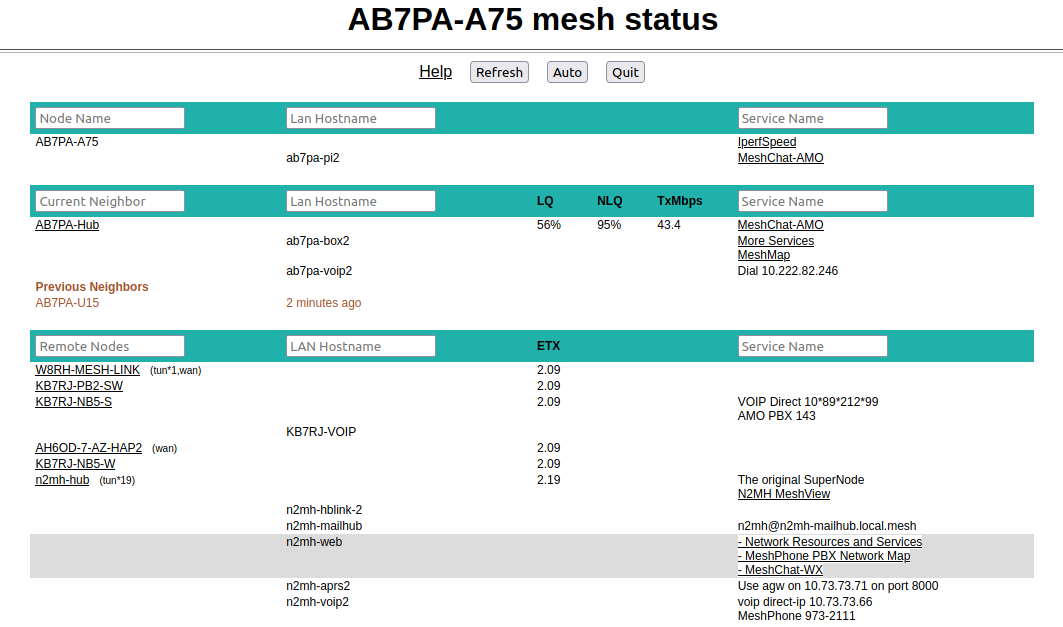
- Your Node
This shows your node as well as any connected LAN hosts and the advertised services available on your node and hosts. You can click any available web links to navigate to the services on your node or LAN hosts. This will be true for any available services in the Current Neighbors or Remote Nodes sections, too. Since this display is slightly wider than before, each row will be highlighted as you hover your cursor over it. This gives a visual indicator for any column entries that are part of the row over which you are hovering.
If you have any hosts for which you selected Do Not Propagate in the DHCP Reservations List, those hosts will be displayed in a light gray color only on your node’s Local Hosts column. If you created any DNS Aliases for your hosts, those aliases will be displayed in a light orange color only on your node’s Local Hosts column. All other hosts will be displayed in the default color for the theme that you are using.
- Current Neighbors
This shows a list of Neighbor Nodes that are directly connected with your node, meaning they are only one network “hop” distant. These nodes may be connected via RF, DtD link, or a tunnel over an Internet connection. It also shows any LAN hosts on your current neighbors as well as any advertised services available on those nodes and hosts.
There are several link quality statistics displayed for each connected node.
LQor Link Quality is your node’s view of the percent of OLSR (Optimized Link State Routing protocol) packets received from the neighbor node. These packets exchange mesh routing and advertised services information, and they include a sequence number that is used to identify missing packets. For example, if 7 of 10 packets sent by the neighbor were received, then the probability for a successful packet transmission from this neighbor is 7/10 = 0.7 = 70%. Be aware that the Quality metric on the Neighbor Status display is calculated differently, so there may not be a perfect alignment when comparing the two quality metrics.NLQor Neighbor Link Quality is the neighbor node’s view of the percent of OLSR packets received from your node. This indicates the quality of the link from the neighbor’s side.TxMbpsor Transmit Megabits per Second is an estimate of the data rate achieved across any RF link with a neighbor node. This column may show zero if the data being transmitted between these nodes is not sufficient for the metric to be calculated.Servicesis the column which displays any available services on the neighbor node or its LAN hosts. You can click on service links to navigate to the webpage for those services on the neighbor node.
In addition to the neighbor node name, there may be a text abbreviation in parentheses that tells how the neighbor node is connected.
(dtd)indicates a Device to Device connection (typically using an Ethernet cable) between the nodes.(xlink)indicates a connection between the nodes that traverses cross-linked devices.(tun)indicates the path to the neighbor node is over an Internet tunnel.(tun*?)next to a mesh node in the Remote Nodes column indicates the node has tunnel links over the Internet to connect mesh islands together.?is a number indicating the number of tunnel connections on that node.(wan)indicates the node has been configured as a Mesh Gateway. Typically this is a gateway to the Internet, but it may also be to another isolated network.
- Previous Neighbors
If there were any Current Neighbors which disconnected within the last 24 hours they will be listed below any nodes that are currently connected. It shows the node name or IP address, as well as how long it has been since a node was actively connected to your node.
- Remote Nodes
This section lists the other nodes on the network that are two or more hops away from your node. Advertised services on nodes and their LAN hosts are also listed. Remote Nodes are sorted by their
ETXor Expected Transmission metric. ETX is an estimate of the number of OLSR packets that must be sent in order to receive a round trip acknowledgement, and it is often referred to as link cost. When sending data the OLSR protocol selects the least cost route based on the lowest ETX in the direction of the final destination.
Searchable Column Headers
As your network grows in size, the length of the Mesh Status display will also grow. At some point it may become difficult to find specific devices or services on the page, especially in the Remote Nodes section. To help alleviate this issue search fields have been provided on several column headers in the Current Neighbors and Remote Nodes tables.
As you enter each character from your keyboard into the search fields, the display will change to show only the entries that match your character or string. The filter is case insensitive, so it will find both upper and lower case entries for the characters you enter.
If you press the Refresh button on the Mesh Status display, your search fields will be cleared. In some cases if you press the Enter key after entering your search string, you may notice that the Mesh Status display is refreshed and your search string is gone – but if you click the field where you entered the search string you may see that the browser has saved that string for future use and it can be selected from a dropdown list. This behavior is browser-dependent, so you may find slightly different behavior depending on the web browser you are using.