Node Status Display
Once you have completed the initial setup on your AREDN® node, you can connect your computer to the LAN port on the PoE and navigate to the following URL: http://localnode.local.mesh. You will be redirected to the Node Status page as shown below.
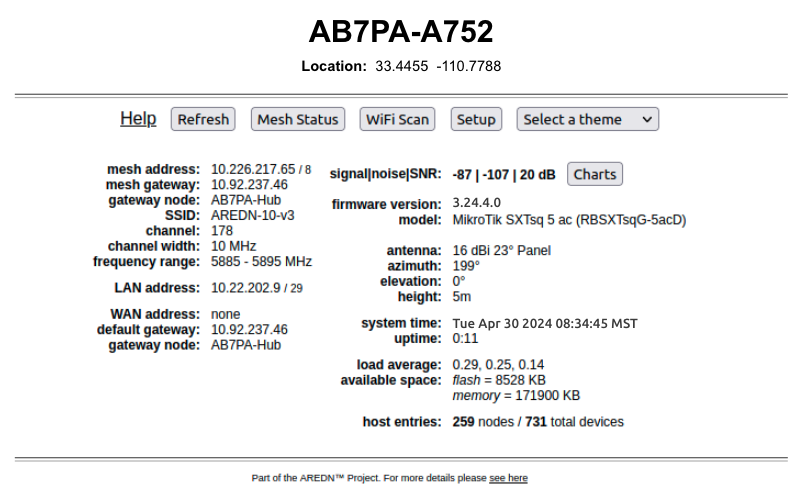
Below the node name bar there are several controls.
- Help
Opens a new window or tab to display the node help page.
- Refresh
Updates the Node Status page with current data.
- Mesh Status
Opens the Mesh Status page showing the neighbor nodes and remote nodes visible on the mesh network, as well as what services are being provided by those nodes.
- WiFi Scan
Displays a list of other 802.11 signals within range of your node. The 802.11 signals may include Access Points, neighbor nodes, and other mesh networks (foreign ad-hoc networks). WiFi Scan is described in more detail below.
- Setup
Navigates to the Setup pages for your node. You will need to supply a username and password to access those pages. The username is always
root, while the password is the one you set during initial node setup. If the node has not yet been configured, the password ishsmm.- Select Theme
AREDN® firmware has several built-in display themes. The default
aredntheme has a gray background with black and red text. Theblack_on_whitetheme is often chosen because it provides the best screen contrast on a computer exposed to direct sunlight.red_on_blackis much better suited for nighttime use since it helps preserve night vision.
Node Settings Summary
The area under the control buttons shows both configuration and network status information. The left column contains the IP address and gateway details for the network interfaces on this node, as well as the SSID, channel, channel width, and frequency range if Mesh is enabled. If WAN Wifi Client is enabled it will also show the SSID and signal strength to the connected Access Point. If LAN AP is enabled then the LAN AP SSID will also be displayed.
The right column contains the Signal Strength readings and other attributes of your node. The signal / noise / ratio shows the strongest neighbor signal strength in dBm from all connected stations, and it is available only when the node is connected to a neighbor node via RF. Click these links for further information about Signal to Noise Ratio and values measured in decibels. There are many factors that impact the network throughput you can expect to achieve, but as a general rule the higher the Signal-to-Noise ratio the better the throughput for your RF links.
Below the Signal Strength readings are the node’s firmware version, hardware model, and antenna info. The system time is displayed, as well as the uptime, which is the time since the last reboot. If an Internet connection or a local NTP server is available, your node’s NTP client will sync its time with that time source.
The load average is the average number of processes that have been running on the node for the last 1, 5, and 15 minutes. available space tells you how much storage space is remaining on your node. flash is the internal non-volatile storage where the operating system, configuration files, and software packages are kept. memory is the amount of RAM available for running processes on the node. host entries shows the total number of devices seen on the network, and the total includes the AREDN® nodes as well as any other networked devices such as computers, VoIP phones, PBX devices, cameras, and other hosts.
Signal Charts
There is a Charts button next to the node’s Signal Strength display, and clicking this button takes you to Signal Charts. This page shows RF signal information in both a realtime and an archived view. The default view shows the average signal of all connected stations in realtime.
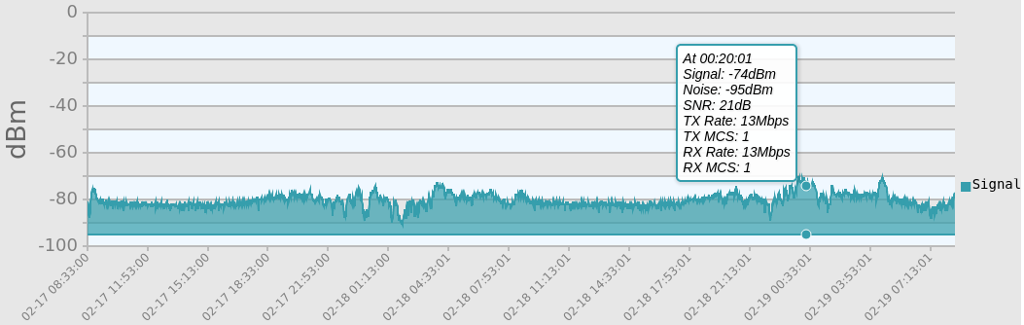
At the top of the charts display there are several control buttons.
- Archive
This button shows the charts for any archived signal data on this node. Statistics are stored on the node in a circular buffer which holds about two days of data.
- Realtime
This button shows the charts for current signal data as seen from this node.
- Quit
This button exits the charts view and takes you back to the Node Status page.
Below these controls you can choose to view the signal strength statistics for individual nodes that are directly connected to your node. Choose the neighbor node from the Selected Device dropdown list. Changing the selected device will automatically reload the chart to show that node’s information.
Hovering over data points within a chart will show additional information for each data point, including Time, Signal, Noise, SNR, TX Rate, TX MCS, RX Rate, and RX MCS. If no traffic is being routed to the neighbor, the Rate and MCS values may be zero until data is available. An MCS value of zero may indicate non-802.11n encoding schemes (ie. 802.11a/b/g).
The small icon with three vertical dots in the upper right corner of the chart allows you to download a snapshot of the chart to a graphic file on your local computer (jpeg or png).
Data shown in the Archive charts is not stored in permanent memory on the node. The node will store approximately two days of archived data, and all data is cleared when a node is rebooted.
If you click and drag your mouse across a region of the chart, the display will zoom into that selected area. This allows you to view data points for a specific time range of your choice. While zoomed, two additional icons will appear in the upper right of the chart. The Pan icon allows you to scroll and pan the zoomed portion of the chart. The Reset icon returns the chart to its normal display mode.
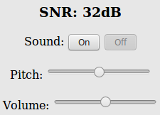
On the left of the Realtime Graph there is an SNR Sound control. Clicking the On button will cause your computer to emit a tone that corresponds to the relative SNR level, with higher pitch tones indicating better SNR. This feature was added in order to provide an audio queue to operators in the process of aligning directional antennas. When your antenna reaches a position at which the highest pitch tone is heard you can lock it down without having to look at the signal graph display, knowing that you are receiving the best signal available. You can also adjust the tone pitch and volume with the sliders on the sound control.
WiFi Scan
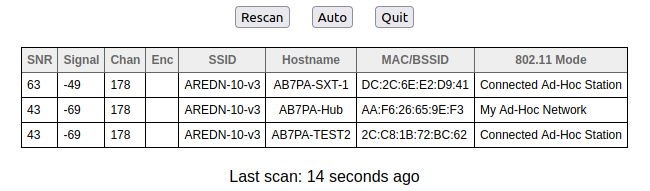
WiFi Scan initiates a passive scan for wifi signals that are within range, but it only reports devices on the same channel width as your node. When installing a node at a new location it is best practice to scan on 5, 10, and 20 MHz channel widths to find all other 802.11 signals in range. This information will help you to pick a channel clear of interference. Several scans may be necessary to find all devices in range. When multiple ad-hoc networks are visible (using different SSIDs or channels), the ID of each 802.11 network is displayed but not the individual nodes.
A passive scan does not transmit probes, so there is no risk that unintended transmissions will interfere with radar stations on DFS channels. Automatic scan mode is available, but running a scan continuously is not recommended if the node is actively routing traffic. Even though the auto-scan is passive and only listens for other beacons across all channels, there is a risk of data loss on the assigned channel.
Attention
With some devices, a scan will momentarily disconnect the wifi from the mesh so the radio is available to perform the scan operation. It is recommended that you perform a scan when connected to the device in some other way.
The scan results from your last scan are retained, along with the relative time since that scan was completed. If you only want to see the results from your last scan, you can go to the Wifi Scan page to view those results without having to initiate a fresh scan. Once a scan has finished, you can click the Rescan button to start a new scan. If you want your node to rescan continually you can click the Auto button. Click Quit to return to the Node Status display.
AREDN® Alert Messages
AREDN® Alert Messages are displayed in a yellow banner on a node’s status page above the node name. There are three types of messages: broadcast messages intended for all nodes, group messages selected by labels in advanced settings and directed messages which are only retrieved by individual nodes. Individual nodes will attempt to pull the messages from the message repository URL once every 12 hours by default. Be aware that there is no guarantee of privacy for these messages, since anyone can view the message repository online. The AREDN® development team also has the ability to post messages which Internet-connected nodes will automatically retrieve.

Mesh nodes without Internet access also have the ability to display Local Alerts. The process for setting up a local message repository is described in the Configuration Deep Dive section, which allows node owners to decide whether to opt in to receive local messages on each of their nodes. If a node has Internet access as well as local messages, then both types of messages will be displayed in the AREDN® alerts banner as shown in the example above. There is also a web front-end application created by Gerard Hickey (WT0F) which runs directly on a node having adequate storage. You can find out more about this application in the Applications and Services Guide under the Other Services section.